
Two recent flash loans on the defi platform Bzx have started a fierce debate about the subject of using uncollateralized loans in a quick trade. Essentially these flash loans are providing people with the ability to borrow crypto without relinquishing any collateral. The scheme was used to exploit funds from the Bzx platform twice, as an individual or group gathered around $954,000 in a matter of four days from well-executed flash loans.
Also Read: Get Ready for the Bitcoin Halving – Here Are 9 Countdown Clocks You Can Monitor
Flash Loans: Attack or Innovative Forms of Defi?
Decentralized finance (defi) flash loans is a hot topic right now, after the lending platform Bzx saw $954,000 siphoned from two flash loans. The first one took place on February 14 and then another Bzx ‘attack’ occurred on February 18. The method of execution called a “flash loan” has been a contentious subject because people don’t necessarily agree that flash loans are an “attack,” “hack,” or “exploit,” because the scheme merely follows the rules of the said contract and loan system. A number of Ethereum proponents believe flash loans are useful and open up new avenues of decentralized finance.
find the flash lenders:
👩🏻👩🏼👩🏽👩🏾👩🏿👩🏻👩🏼👩🏽👩🏾👩🏿
👨🏻👨🏼👨🏽👨🏾👨🏿👨🏻👨🏼👨🏽👨🏾👨🏿
👧🏻👧🏼👧🏽👧🏾👧🏿👧🏻👧🏼👧🏽👧🏾👧🏿
👦🏻👦🏼👦🏽👦🏾👦🏿👦🏻👦🏼👦🏽👦🏾👦🏿can’t find them?
that’s because they live among us, looking like normal people. the only real difference is they now have the access to whale-like liquidity.
— stani.eth ’Flash Loans Maximalist’ Kulechov 👻 (@StaniKulechov) February 20, 2020
During the first big flash loan, the so-called hacker got 10,000 loaned ETH from the application Dydx and snagged 112 wrapped bitcoin (WBTC) from the defi protocol Compound. The individual then sent around 1,300 ETH to Bzx’s Fulcrum trading platform and then borrowed 5,637 ETH via Kyber’s Uniswap for around 51 WBTC. From here, that particular move caused significant slippage (the difference between the expected price of certain trades and the price of trade execution) within the market. After that, the individual made a profit from the 112 WBTC loan they first obtained from Compound and raked in roughly $318,000 in profit. This single transaction allowed the individual to easily pay back the 10,000 ETH from Dydx.
1/ WHAT WE KNOW SO FAR: There was a second attack. This attack was completely different from the first. This time it was an oracle manipulation attack, a modified version of the original exploit we worked closely with @samczsun to fix: https://t.co/lDcyDQf44i
— bZx (@bzxHQ) February 18, 2020
Now as confusing as all that sounds, basically a flash loan is the ability to leverage uncollateralized defi capital in order to profit from a well-executed dex trade. The process is done very quickly and efficiently in order to curb the risk of losing funds during execution. The person performing a flash loan can use their assets to drop the price across markets in order to trigger defi apps with oracles to sell at the desired spot price. Defi apps like Bzx, Dydx, and Compound use price oracles to determine the prices across various decentralized exchanges (DEX) like Kyber’s Uniswap.
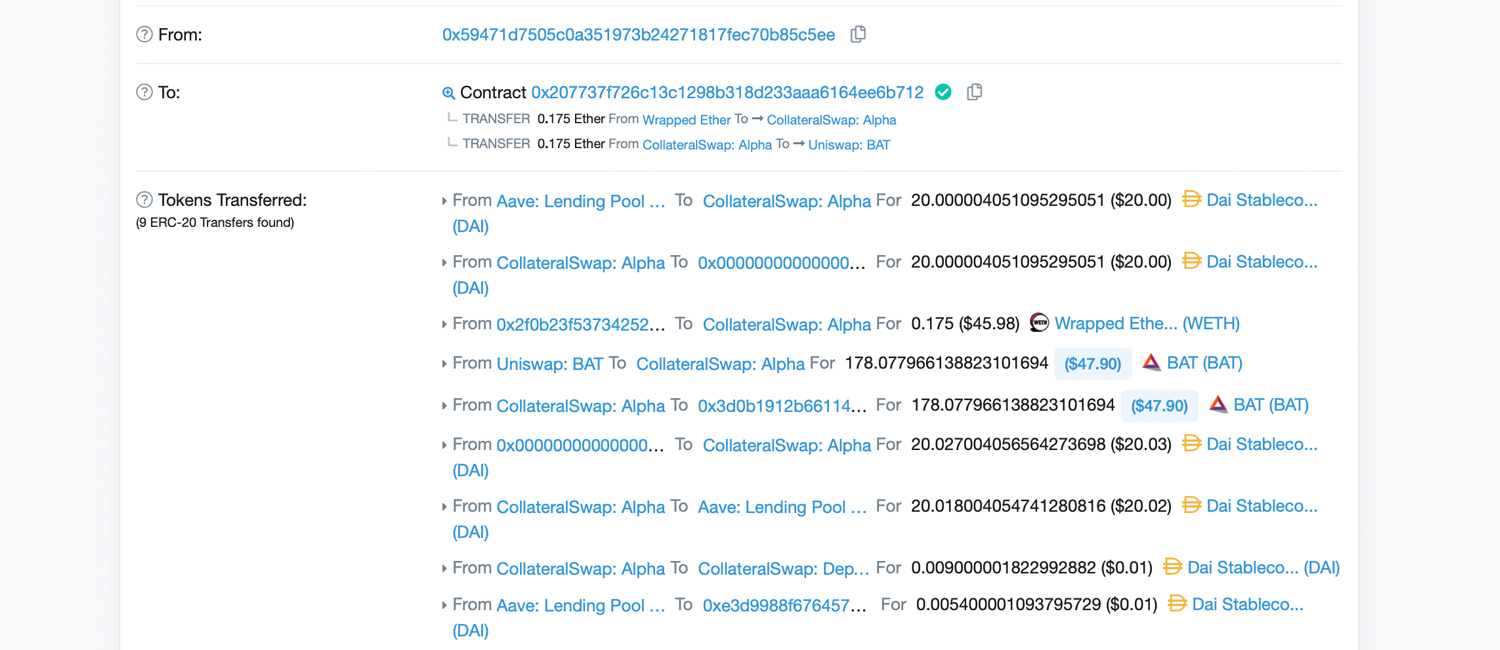
Behind the scenes of a @MakerDAO collateral swap using @AaveAave Flash Loans, @UniswapExchange and @chainlink oracles 📸 @daveytea @RyanSAdams @econoar @nanexcool @EthereumMemes $LEND $LINK $ETH #Woah pic.twitter.com/NyKo1JHV6x
— Jordan LG 👻 (@JordanLzG) February 20, 2020
The pricing information often has large discrepancies across exchanges, which allow for market anomalies like slippage and arbitrage. The speed of a flash loan’s execution is so fast because the loan, trade, settlement, and profits are executed simultaneously in a single transaction. The individual who performed the first massively sized flash loan against Bzx simply borrowed funds from the defi platform’s smart contract without any collateral and they were able to pay the loan back in a single transaction.
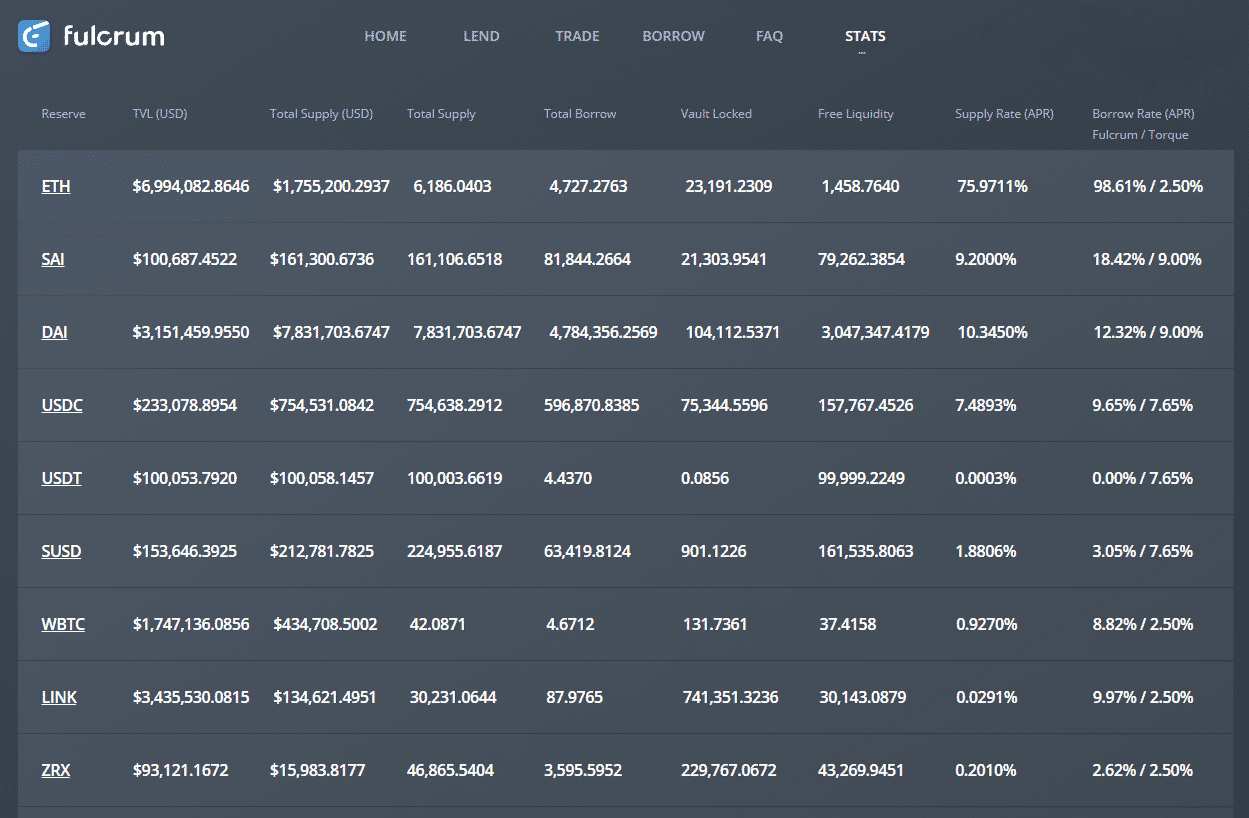
Flash Loan Demos, Inflation and Deflation, and the Flavors of Flash Loans
Following the two massive flash loans that took place on Bzx’s Fulcrum trading platform, the crypto community continues to debate the topic on social media and forums with great fervor. There has been deep analysis and studies done on the subject of flash loans and people debating about whether the acts are malicious. Moreover, some individuals have shown the public how simple it is to execute a flash loan using a defi platform and DEX.
Flash loans are communism. Only rich ppl are allowed to manipulate markets
— Joseph Delong (@josephdelong) February 18, 2020
On Twitter, Fiona Kobayashi showed crypto enthusiasts how she executed a small flash loan. In a single transaction, Kobayashi got a loan of ETH from the platform Aave with no collateral. She then exchanged it for BAT tokens on Uniswap and moved the BAT to Makerdao platform as collateral and withdrew ETH collateral from Maker. After that, Kobayashi repaid her loan on Aave and used Rosco Kalis’ revoke.cash platform to “revoke the original vault’s ERC allowances.”
“Not sure why I ended up with an extra $4.70 worth of DAI, it was supposed to be a net neutral flash loan,” Kobayashi tweeted.
A few people think flash loans can cause inflation, similar to how central banks lower circulating supply and then they simply adjust rates. “Inflation happens, but so does deflation too, [the] Fed can lower circulating supply at any time and raise interest rates,” an individual remarked after the Bzx flash loan. “Flash loan exploit inflation is crazy,” another person tweeted on February 18. The reason people believe that flash loans could cause erratic inflation and deflation is because when a flash loan is executed, the profits are being taken from somewhere within the chain of events in the single transaction. Oracles are easily being gamed and developers may have to come up with new ideas to gather verifiable price data.
Can someone flash loan attack ProgPoW?
— eric.eth (@econoar) February 22, 2020
Emilio Frangella from the Aave Protocol wrote a blog post about the subject on February 12 and he said that flash loans were innovative. “Flash Loans have especially captured the attention of the defi crowd and we expect other defi protocols to follow our lead and implement their flavors of flash loans as well. Like any other building block of Ethereum composability, flash loans quickly allowed new creative ideas to become reality,” Frangella wrote. The Aave Protocol team member further added:
Prime examples of this are Arbitragedao (a DAO with the goal to market make arbitrage opportunities by leveraging the flash loans) and the Maker Vault collateral swapper (which allows you to swap your collateral from ETH to BAT in one transaction).
What do you think about flash loans in the crypto world? Let us know what you think about this topic in the comments section below.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It is not an offer or solicitation of an offer to buy or sell, or a recommendation, endorsement, or sponsorship of any products, services, or companies. Neither the company nor the author is responsible, directly or indirectly, for any damage or loss caused or alleged to be caused by or in connection with the use of or reliance on any content, goods or services mentioned in this article.
Image credits: Shutterstock, Etherscan, Twitter, Fair Use, Bzx Fulcrum, and Pixabay.
Did you know you can verify any unconfirmed Bitcoin transaction with our Bitcoin Block Explorer tool? Simply complete a Bitcoin address search to view it on the blockchain. Plus, visit our Bitcoin Charts to see what’s happening in the industry.
The post Understanding Defi Flash Loans: Complex Attacks, Inflation and Composable Systems appeared first on Bitcoin News.
via Jamie Redman
0 comments:
Post a Comment